


A/a Gradient

คำอธิบายของA/a Gradient
The variables in this App. are :
RQ :Respiratory Quotient (approx 0.8 at normal physiological state)
PB : Atmospheric pressure.(760 mm Hg at sea level.)
FiO2 : Fraction of Inspired Oxygen. (0.21 at room air.)
PAO2 : Alveolar Oxygen tension
PaO2 : Arterial oxygen tension
These can be independently changed and the reflection of these changes can be seen in the alveolar – arteriolar gradient and PaO2 / FiO2 ratio.
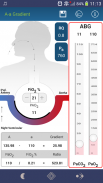
A-a oxygen gradient : The alveolar arterial (A–a) oxygen gradient is a measure of oxygen transfer across alveolar capillary membrane (“A” denotes alveolar and “a” denotes arterial oxygenation). It is the difference between the alveolar and arterial oxygen tension.
A-a oxygen gradient = PAO2 - PaO2.
PaO2 is derived from ABG while PAO2 is calculated.
PAO2 = (FiO2 x [PB - PH2O]) - (PaCO2 ÷ RQ)
[PH2O is the partial pressure of water (47 mm Hg)] & PaCO2 is partial pressure of Carbon di oxide in arterial blood.
A-a gradient varies with age and can be estimated from the following equation, assuming the patient is breathing room air.
A-a gradient = 2.5 + 0.21 x age in years.
A-a gradient increases with higher FiO2.
PaO2/FiO2 ratio : It is a measure of Oxygen transfer across the alveolar capillary membrane. Normal PaO2/FiO2 ratio is 300 to 500 mmHg. Values less than 300 mmHg indicating impaired gas exchange and values less than 200 mmHg indicates severe hypoxemia.
"Alveolar arterial membrane is depicted in this App. as a BLACK LINE (This is purely a conceptual representation of ventilation-perfusion relationship).The thickness of this Black Line is shown to vary depending on the variations in A-a gradient"
ตัวแปรใน App นี้ คือ:
RQ: ความฉลาดทางระบบทางเดินหายใจ (ประมาณ 0.8 ที่รัฐทางสรีรวิทยาปกติ)
PB: ความดันบรรยากาศ (760 มิลลิเมตรปรอทที่ระดับน้ำทะเล.).
FiO2: เศษของออกซิเจนแรงบันดาลใจ (0.21 ในอากาศในห้อง.)
PAO2: ความตึงเครียดออกซิเจนถุง
PaO2: ออกซิเจนหลอดเลือดแดง
เหล่านี้สามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงได้อย่างเป็นอิสระและสะท้อนให้เห็นถึงการเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้สามารถเห็นได้ในถุง - การไล่ระดับสีหลอดเลือดแดงและอัตรา PaO2 / FiO2
Aa ไล่ระดับออกซิเจนที่: ถุงแดง (A-) ลาดออกซิเจนเป็นตัวชี้วัดของการถ่ายโอนออกซิเจนผ่านเยื่อหุ้มเซลล์เส้นเลือดฝอยถุง ("A" หมายถึงถุงและ "เป็น" หมายถึงออกซิเจนแดง) มันเป็นความแตกต่างระหว่างถุงและความตึงเครียดออกซิเจนเส้นเลือด
A-ลาดออกซิเจน = PAO2 - PaO2
PaO2 มาจาก ABG PAO2 ขณะที่มีการคำนวณ
PAO2 = (FiO2 x [PB - PH2O]) - (PaCO2 ÷ RQ)
[PH2O เป็นความดันบางส่วนของน้ำ (47 มิลลิเมตรปรอท)] และ PaCO2 คือความดันบางส่วนของคาร์บอนดิออกไซด์ในเลือดแดง
ไล่ระดับ Aa แตกต่างกันไปตามอายุและสามารถประมาณได้จากสมการต่อไปนี้สมมติว่าผู้ป่วยจะหายใจอากาศในห้อง
A-ลาด = 2.5 + 0.21 x อายุในปีที่ผ่าน
A-การเพิ่มขึ้นของการไล่ระดับสีที่มี FiO2 ที่สูงขึ้น
PaO2 / อัตราส่วน FiO2: มันเป็นตัวชี้วัดของการถ่ายโอนออกซิเจนผ่านเยื่อหุ้มฝอยถุง ปกติ PaO2 / อัตราส่วน FiO2 เป็น 300-500 มิลลิเมตรปรอท ค่าน้อยกว่า 300 มิลลิเมตรปรอทแสดงให้เห็นความบกพร่องการแลกเปลี่ยนก๊าซและค่าน้อยกว่า 200 มิลลิเมตรปรอทบ่งชี้ hypoxemia รุนแรง
"เมมเบรนของหลอดเลือดถุงเป็นที่ปรากฎใน App นี้. เป็นเส้นสีดำ (นี่คือหมดจดเป็นตัวแทนความคิดของความสัมพันธ์ของการระบายอากาศ-perfusion) ความหนาของเส้นสีดำได้โดยเริ่มต้นนี้แสดงให้เห็นว่าแตกต่างกันไปขึ้นอยู่กับรูปแบบในการไล่ระดับสี Aa ว่า"

























